Trochanteritis (greater trochanteric bursitis) is one of the sports injuries that develops mainly in marathons and soccer, if you think you suffer from Trochanteric Bursitis, continue reading this article and find out about this injury and know how it can be treated at FisioClinics Palma from Mallorca.
What is Trochanteritis?
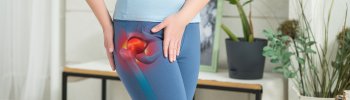
Trochanteritis could be defined as the inflammation of the bursa of the greater trochanter in the hip, it generates acute pain that in some cases does not subside or decrease with rest. The pain arises when the trochanteric bursa, which has the function of smoothing movement, has inflammation, it can be caused by a variety of causal factors that we will discuss later.
What are the symptoms of Trochanteric Bursitis?
Trochanteric Bursitis usually causes pain and limits movement of the hip, but the specific symptoms will vary depending on the inflammation. Also called Trochanteritis, it occurs over several hours to several days. Movement or touching the swollen site on the hip usually causes pain. In addition, the pain associated with Trochanteric Bursitis tends to be worse at night, especially when the person is lying down or lying on their side for some time. If the tendons around the hip bone are inflamed, symptoms may be worse.
What Causes Trochanteric Bursitis?
To understand the cause of Trochanteric Bursitis, it is necessary to know the dissection of the affected hip and lower extremities. The first thing to clarify is the greater trochanter is a region that is constantly subjected to strong mechanical stress on the connecting parts of many muscles and ligaments.
Between the greater trochanter and the gluteal muscle group there is a bag that surrounds the synovial fluid and has the function of improving the sliding of the movement of the hip joint, this bag is the bursa of the greater trochanter.
Trochanteritis of the greater trochanter is caused by excessive repetitive flexion exercise and extension movement of the hip joint, overuse (running too much), sometimes the bursa wall thickens. If abnormal exercise or stress occurs on the damaged bursa, the inflammation tends to worsen. If the pain or swelling lasts for a long time, it will be difficult to move the joint and muscle strength will decrease.
How is the medical diagnosis of Trochanteritis made?
A specialist can assess the painful area by touching the surroundings of the bursa close to the skin, or if the movement of a specific joint, such as moving a bag in a deep position or pressing it, is painful is suspected Trochanteritis. If the bursa is visibly inflamed, fluid may need to be removed from the bursa, and examination of the sample will investigate the cause of the inflammation (such as infection and gout). Normally, the x-ray examination is done only when the bursitis is persistent or chronic.
 Physiotheraphy
Physiotheraphy Osteopathy
Osteopathy Massage
Massage Lymphatic
Lymphatic Group classes
Group classes Home
Home Baby
Baby